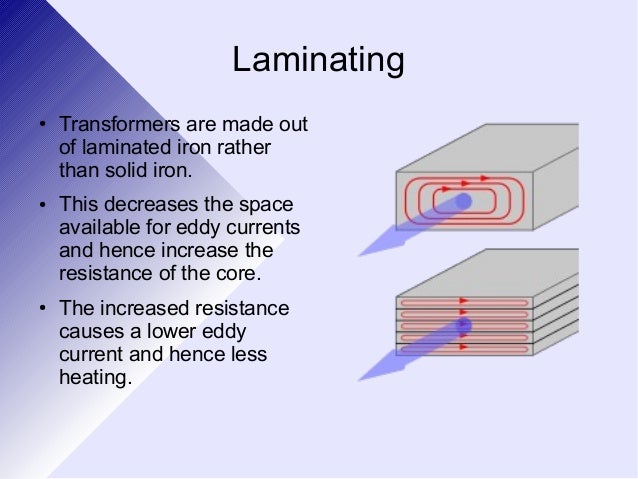
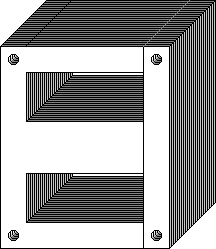
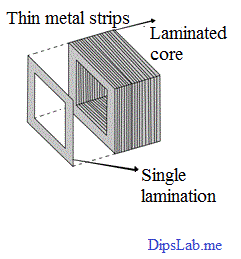
Laminated transformer core the core of a laminated transformer consists of a stack of punched sheet alloy made of iron and nickel the laminations.
Iron core power transformer is laminated to reduce.
Power factors of both the transformers will be same.
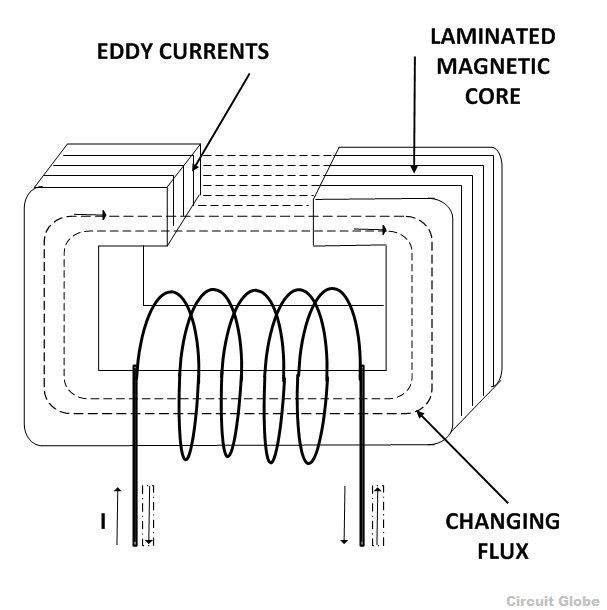
Eddy current losses are proportional to the frequency and magnitude of the current in the core of the transformer.
Question is a transformer core is laminated to options are a reduce hysteresis loss b reduce eddy current losses c reduce copper losses d reduce all above losses e leave your comments or download question paper.
The eddy currents cause energy to be lost from the transformer as they heat up the core meaning that electrical energy is being wasted as unwanted heat energy.
For example dropping a transformer on one of its edges on concrete could short the laminates.
The core of the transformers needs to be laminated to reduce the eddy current that has arisen from the induced voltages through the core reducing the heat loss of the whole core which is why the core of the transformers is laminated to restrict the eddy currents flowing through it.
Therefore solid iron cores are not used in transformers or inductors they are replaced by laminated or powdered iron cores or nonconductive cores like ferrite.
The current flowing through the resistance of the metal heats it by joule heating causing significant power losses.
When handling transformers with the core exposed care should be taken not to break the insulating integrity of the core.
Laminating the iron core eddy current losses within a transformer core can not be eliminated completely but they can be greatly reduced and controlled by reducing the thickness of the steel core.
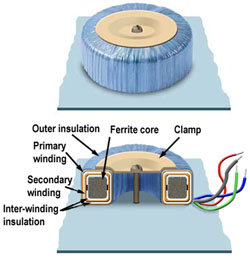
Provide support to windings.
The core is made from e and i lamination.
Why iron core is thin laminated in transformer the iron core transformer has higher permeability thus it is applied in transformer in place of air core in modern transformer.
The percentage of nickel is adjusted to give a reduced energy loss when the core is magnetised by the magnetic field produced when the primary winding is energised.
A transformer core is laminated to a reduce hysteresis loss b reduce eddy current losses c reduce copper losses d reduce all above losses.
The core is laminated to reduce these to a minimum as they interfere with the efficient transfer of energy from the primary coil to the secondary one.